Venomous bites and stings from spiders, scorpions, snakes, lizards and jellyfish — even caterpillars, snails and octopuses — harm hundreds of thousands yearly and kill many 1000’s globally.
However these animals’ poisons are poised to assist present a brand new wave of medicines to deal with all the things from most cancers to coronary heart illness — even to decelerate ageing.
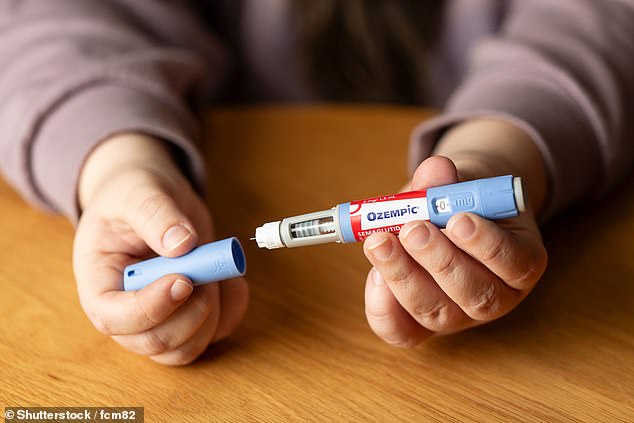
This isn’t just a few distant hope. Already a deadly animal venom is the key behind the blockbuster weight-loss drug semaglutide, higher often called Wegovy and Ozempic.
What’s extra, viper venom underlies medication known as ACE inhibitors, that are taken by 1000’s of individuals within the UK for hypertension.
Ozempic and Wegovy earned their maker a startling £15billion final 12 months, with a swarm of superstar endorsements from TV character Sharon Osbourne and former pop star Boy George to billionaire investor Elon Musk.

The key of Ozempic’s success lies in the Gila monster, which grows as much as 2ft lengthy and is the one venomous lizard native to the US
Ozempic and Wegovy earned their maker a startling £15billion final 12 months, with a swarm of superstar endorsements from stars together with Sharon Osbourne and Elon Musk
However the secret of those weight-shrinking medication’ success lies in a mean-looking reptile, the Gila monster, which grows as much as 2ft lengthy and is the one venomous lizard native to the US.
Human fatalities from its chew are uncommon, although earlier this 12 months coroners in Colorado reported {that a} native man, Christopher Ward, 34, died ‘as a consequence of issues of Gila monster envenomisation’ after being bitten on the hand by one which he had been holding illegally as a pet.
A chew from the venomous jaws may cause swelling, intense burning ache, vomiting, dizziness, a speedy coronary heart price and plummeting blood stress. However Gila venom additionally enlarges and over-stimulates the pancreas — the organ that makes the hormone insulin which helps regulate starvation and blood sugar ranges.
Practically 35 years in the past, Dr John Eng, an endocrinologist on the Veterans Affairs Medical Middle in New York, realised this meant {that a} chemical within the venom may need twin use — the lizard makes use of it not solely as a poison, but additionally as a hormone to regulate its manufacturing of insulin very tightly.
Gila monsters, of their desert habitat, catch prey sometimes. However throughout lengthy intervals of hunger they’re able to decelerate their metabolism and preserve fixed blood sugar ranges. Dr Eng questioned if that shut management of insulin might assist people with sort 2 diabetes, the place their blood sugar ranges have gone uncontrolled.
He trawled by means of the a whole bunch of chemical elements in Gila venom till he recognized a small protein that he known as exendin-4.
This seemed just like glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), a hormone discovered within the human pancreas that regulates insulin and urge for food when our blood sugar ranges are excessive, resembling instantly after a meal. However whereas GLP-1 stays energetic within the human physique for about two minutes, exendin-4 stays energetic for hours, suggesting it might have a long-acting impact on regulating blood sugar and urge for food so that folks really feel satiated regardless of consuming much less.
In 2005, Dr Eng’s work culminated in a drug synthesised from exendin-4 to deal with sort 2 diabetes. It was launched because the world’s first GLP-1 mimicking drug, exenatide (additionally recognized by the model identify Byetta).
Rival drug firms vied to make their very own exenatide-type medication with larger effectiveness. The primary clear winner to emerge was semaglutide, made by the Danish pharmaceutical firm Novo Nordisk and marketed underneath the model identify Ozempic.
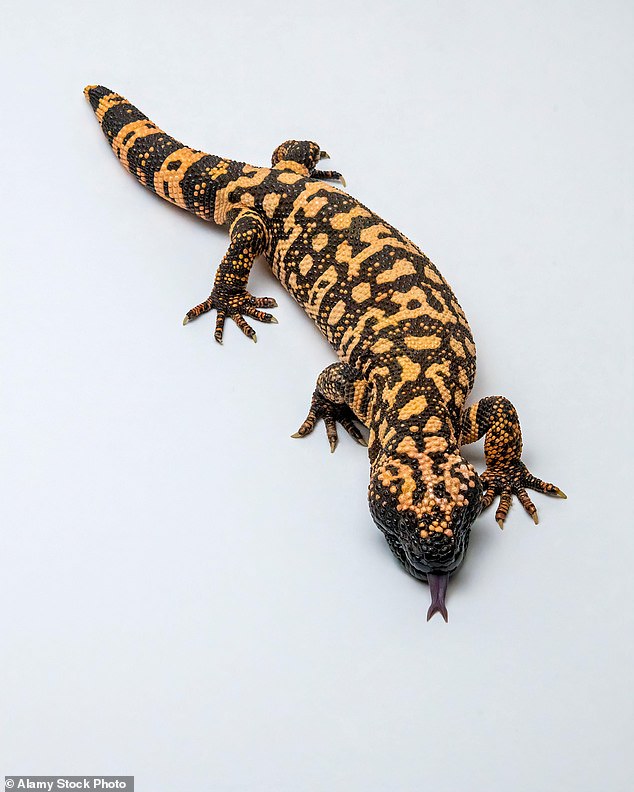

A chew from the venomous jaws of a Gila monster may cause swelling, intense burning ache, vomiting, dizziness, a quickening coronary heart price and plummeting blood stress

Scientists are mining venoms for brand spanking new therapies for quite a few ailments in a scientific subject often called ‘venomics’
This proved extremely efficient each towards sort 2 diabetes and urge for food — and later a unique dose, marketed as Wegovy, proved efficient as a weight-loss drug.
Such success has bolstered the efforts of scientists who’re mining venoms for brand spanking new therapies for quite a few ills. This subject even has its personal identify — venomics.
Greater than 220,000 species, or roughly one sixth of all animal species on earth, are venomous, and every creature’s venom is exclusive.
For instance, whereas a spider’s could comprise 1000’s of energetic chemical compounds, a scorpion’s may need solely a number of hundred.
These venoms are the results of millennia of competitors between predator and prey, the place every time one evolves a brand new immune defence the opposite develops a brand new technique of poisoning.
Dr John Finger, a biologist at Auburn College in Alabama, made an astonishing discovery in 2020 when he reported how alligators have advanced chemical compounds of their blood that really block lethal snake venom.
‘This permits alligators to eat venomous pit vipers they usually could not succumb to getting bitten by them,’ Dr Finger wrote within the Journal of Herpetology.
Snake venom could maintain monumental potential for brand spanking new medication.
In 1981, captopril was launched as the primary drug developed from animal venom — on this case the jararaca snake, a species of South American pit viper. Scientists had observed that its chew made its victims’ blood stress plummet, and researchers found the venom contained chemical compounds that forestall our our bodies from making a hormone known as angiotensin 2.
This substance narrows the blood vessels, and blocking it causes them to chill out, which lowers blood stress because the vessels dilate extra simply.
The drug synthesised from the viper venom grew to become the primary of a brand new class of oral drugs known as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors. GPs within the UK now challenge about 65million prescriptions for them every year.
In the meantime, different venoms have offered equally revolutionary drug remedies, with many extra exhibiting nice promise for the longer term. Listed here are a few of the most vital breakthroughs…
Octopus
The venom of an Australian octopus might assist deal with deadly melanoma pores and skin cancers.
Dr Maria Ikonomopoulou, head of the Translational Venomics Group on the IMDEA Meals Institute in Madrid, is at the moment creating a drug from venom utilized by the southern sand octopus to defend itself from sea anemones.

The southern sand octopus’s venom is used to defend itself from sea anemones – however may be capable of cease melanoma tumours rising
Referred to as Octpep-1, it has been proven in laboratory experiments to have the ability to cease melanoma tumours rising.
A report within the British Journal of Pharmacology stated it appeared to work towards melanomas pushed by a mutation in a gene known as BRAF V600E, which is concerned in about half of circumstances of melanoma.
‘It’s notably thrilling as a result of Octpep-1 particularly targets most cancers cells and solely minimally results wholesome cells,’ Dr Ikonomopoulou instructed Good Well being.
‘That is very useful, as a result of current medication for one of these most cancers could be considerably poisonous, which limits the quantities sufferers can obtain.’
Dr Ikonomopoulou can also be exploring how venoms from marine animals may very well be used to create anti-ageing medication by focusing on so-called zombie cells within the physique that are alive however don’t perform as they need to.
‘There’s big curiosity on this subject of science,’ she provides.
Spiders
An Australian spider which produces venom that’s among the many world’s most deadly additionally has main potential as a remedy for coronary heart assault and stroke.

The funnel net spider’s venom comprises 3,000 energetic chemical compounds – making it one of the advanced on the earth
The Okay’gari funnel net spider was solely found in 1995, when somebody was bitten by one. Scientists then discovered that its venom comprises about 3,000 energetic chemical compounds, making it one of the advanced on the earth.
In January, researchers at Queensland College printed a research within the European Coronary heart Journal which confirmed {that a} substance extracted from the venom, known as Hi1a, protects cells in components of the center which are broken by coronary heart assault.
The idea is that this may very well be injected into tissue instantly after a coronary heart assault, or additionally to guard the mind after a stroke.
‘Hi1a might scale back injury to the center and mind throughout coronary heart assaults and strokes by stopping cell dying attributable to an absence of oxygen,’ says Glenn King, a professor of molecular bioscience and one of many investigators.
Snakes
Snakes are widespread with researchers due to the big quantity of venom they produce in contrast with smaller animals.

Tirofiban is derived from the venom of a saw-scaled viper, and may cease dangerous clots forming within the arteries after a coronary heart assault
Tirofiban, a extensively used drug derived from the venom of the saw-scaled viper, was first authorized in Europe and the UK 25 years in the past.
This infamous viper is accountable for probably the most snakebite deaths on the earth, as its venom causes catastrophic inside haemorrhaging so victims can swiftly bleed to dying.
In 1987, scientists at Temple College Faculty of Drugs, in Philadelphia, reported how a chemical within the venom, known as echistatin, can forestall human blood platelets sticking collectively and clotting.
This led to the event of tirofiban, which prevents dangerous clots forming within the arteries within the wake of coronary heart assaults, or whereas sufferers are present process surgical procedure to deal with a blocked coronary artery.
In February, on the Worldwide Stroke Convention in Arizona, researchers from China reported that giving sufferers tirofiban promptly after strokes can shield their brains from additional injury higher than the present remedy, aspirin.
Snails
Till ziconotide, a robust painkiller derived from sea snail venom, was authorized for human use in Europe in 2006, no new medication for persistent ache had been launched for greater than 4 many years.
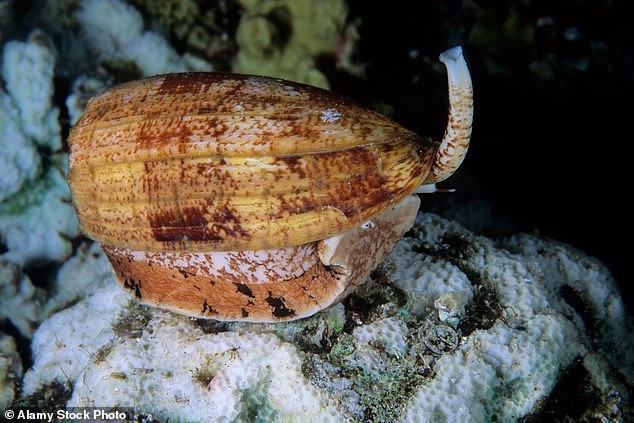

Cone snails have one of many deadliest stings on earth, which might paralyse fish earlier than the snail eats it complete
Ziconotide relies on chemical compounds in a toxin produced by the cone snail, which has one of many deadliest stings of any creature on Earth. The snail makes use of its venom to paralyse fish earlier than swallowing them complete.
In people, the sting may cause doubtlessly deadly paralysis of the lungs.
Scientists on the College of Utah, who analysed it within the late Nineteen Nineties, discovered that sure chemical compounds within the poison also can block ache by stopping nerve cells from sending ache indicators to the mind.
The drug can, nevertheless, solely be injected instantly into the fluid surrounding the spinal wire, by means of a small pump worn by the affected person, which is each painful and invasive. It’s subsequently reserved for these struggling excessive ache, resembling most cancers sufferers.
Caterpillars

The ASP caterpillar is roofed in hairs often called its ‘poisonous toupee’
ASP caterpillars, which stay on oak and elm timber in North America, have lengthy hairs that locals name ‘poisonous toupees’.
These bushy creatures use these prickly spines to inject sturdy venom into their victims. Sufferers liken its impact to touching burning coals or being hit with a baseball bat, and it will probably result in hospitalisation.
However now the caterpillar venom may present an important new strategy to get life-saving medicines inside human cells.
Final 12 months it was reported, within the journal Proceedings of the Nationwide Academy of Sciences, that the venom of asp caterpillars comprises a protein that may poke holes in cells. The caterpillars, which develop into flannel moths, use this mechanism to make their victims’ cells ship debilitating ache indicators to their brains.
Dr Andrew Walker, a molecular bioscientist at Queensland College, says that this novel mechanism could ‘get medication inside cells the place they should work’.
This would possibly, for instance, allow powerfully poisonous most cancers medication to be focused exactly at tumour cells with out harming surrounding wholesome cells.


